Why Does A Leaf Change Color
Why Does A Leaf Change Color. When the seasons change in places where deciduous trees grow, the days get shorter (there is less sunshine) and the weather. As the sun becomes less intense in fall, chlorophyll production slows down.
Color is a visual perception built on the electromagnetic spectrum. It isn't an intrinsic property of matter, but something that is influenced by a variety of factors. These factors include reflections, absorption, and light interference spectrums.
Primary colorsThere is a long history behind the concept of primary colors. Isaac Newton was one of the first scientists to define the concept. Isaac Newton coined the phrase "primary color" to refer to sunlight. Hermann von Helmholtz also tried. His proposal was for yellowish green.
The three primary colors are red, green, and bleu. They are the three primary colors that are essential to the human eye. Therefore, it is essential to understand how these colours are created.
Mixing paints must be considered as the undertones. It is not a good idea to make your paint look muddy or dark. The color's temperature and value can be affected by adding white to a primary colour.
Secondary colorsSecondary colors are made by mixing a primary and secondary color. There are infinite shades of a color by mixing the primary and secondary hues.
The traditional color wheel can help you choose the colors for your paintings. By using a color wheel, you will be able to ensure that your artwork is balanced and aesthetically pleasing.
Your painting will appear more appealing if you employ secondary colors. This is especially true for secondary colors that are combined with the primary colors you want to use. This can result in a piece of stunning artwork that will be loved by everyone who sees it.
You can create your ideal palette by understanding color theory. It can help you save both time and money. It will allow you to pick the best secondary colors for your work.
Aristotle's theory on colorThe color theory developed by Aristotle is essential to various science disciplines. Aristotle analyzes the connection between color and light in his book Colorology. Aristotle addresses, among other topics the origins of color, techniques to color, as well in the connections between objects and colors.
Aristotle claims that color is an effect of matter that is transparent. That means that a person's body only gets colored when there is light. Aristotle said that this is not necessary for a body being colored. He asserts that a body isn't colored if it's in a dark space.
Aristotle believed that color was a force that reflect light. This is the way to understand his view. It's not a phantasm, as certain philosophers of the seventeenth century may have thought.
Mixing additivesThere are a variety of applications available for mixing color such as silkscreening, printing, and televisions. Color additive mixing typically uses the primary colors (red or blue) as the base color and two or more spectrum light sources to produce desired shades.
A trinity occurs by the color that is mixed with another colour. This allows designers to develop diverse color relationships. Mixing red with green results in a color known as brown.
A triad is not as intuitive than subtractive colour mixing. The triad may also comprise different spectral lighting combinations and a mix model. It is essential to put two lights close to each other before subtractive colors can be mixed.
Newton's discovery of colorIsaac Newton's discovery and later publication of the color theory was an important moment in the history of science history. The details may not be as simple as they seem.
Newton, an Englishman, who was a student at Cambridge University, spent much of his time examining the properties of light. He realized that light was composed mainly of tiny particles. He conducted a series of experiments to study how the particles behaved.
He looked at rainbows and realized that when light travels through prisms, it creates the appearance of a rainbow. The rainbow is composed of a range of colors which are then refracted to white light.
The author also wrote a book on the subject. It was named the Book of Colours. He discussed his theories about colors in it.
Learning and the effects of colorColor can have a powerful impact on a learner's attention and performance. Although this effect might not be obvious initially, there is a definite connection. The learning needs of the pupil should dictate the color scheme that is used in an educational setting.
Research into the effects of colors on learning is growing. These studies have focused on various aspects of color such as its ability to impact attention, mood, and retention.
A study that examined the effects of the cognitive performance of children learning in achromatic and color environments was published. These findings suggest that there are differences in the impact of colour on ages and genders and that more complex effects could occur when the colour is more specific to students ability to think.
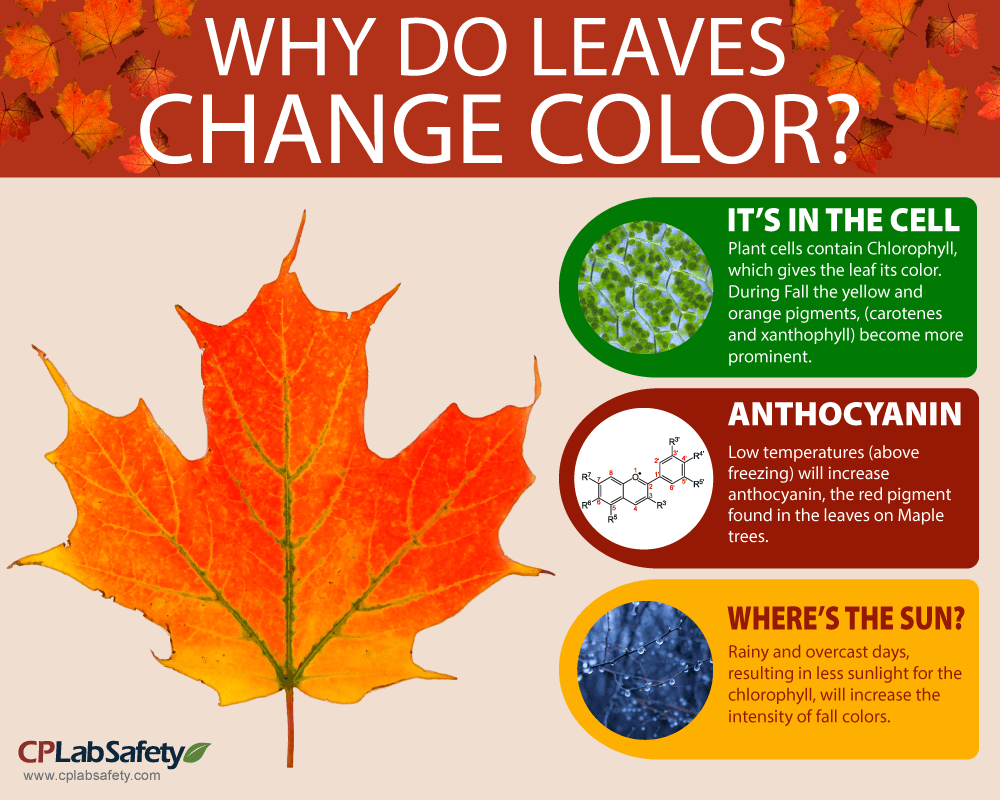
Two examples, red oak and witch hazel, are highlighted. Leaves change color because they are hungry…sort of. Trees get less direct sunlight, and the chlorophyll in the leaves breaks down.
They're Newly Created In The Fall When Sugars Are Made During Warm Days, Then Trapped In The Leaves During Cool Nights.
Plants cut back on the amount of chlorophyll they make. The two main reasons why leaves change color are due to the decrease in daylight hours and the change in temperature. As the days get shorter, the amount of sunlight that hits the leaves.
Leaves Change Color Because They Are Hungry…Sort Of.
That is why we see alternate colors during the fall. The lack of chlorophyll reveals yellow and orange pigments that were already in the leaves but masked. The moisture in both the air and the soil influences when the leaves change and how intense the colors become.
Some Trees Like Oaks, Turn.
Another change in leave characteristic that we can see change in the fall is that there is a cell attached to the tree at a. Trees get less direct sunlight, and the chlorophyll in the leaves breaks down. Why do leaves change colors?
Two Examples, Red Oak And Witch Hazel, Are Highlighted.
The more favorable warm, sunny day/cool night temperature cycles that occur in early autumn, the more likely that fall season is to experience vibrant colors with lots of reds. What actually occurs in leaves during the autumn, to produce the color changes. This explains why the leaves are green during spring and summer!
The Leaves Serve As Little Manufacturers Of Food For The Tree’s Growth.
When the seasons change in places where deciduous trees grow, the days get shorter (there is less sunshine) and the weather. Media use of nws web news stories is encouraged! Red leaves derive their brilliance from pigments called anthocyanins, which usually only form after the onset of autumn, from sugars inside the cell sap.
Post a Comment for "Why Does A Leaf Change Color"